
David Lehrer June 10, 2025
This summer we are excited to announce new funding to support research on low-carbon materials and adaptive reuse. We also share new media that disseminates our work, along with updates on our growing membership, awards and publications.
More

David Lehrer March 10, 2025
In this edition of Centerline we share recent news about staff recognition, funding to create radiant system guidelines, and highlights of new publications on embodied carbon, HVAC innovations, insights and marginal emissions. We also have updates on conferences and other inspiring gatherings, including the ‘Women of Carbon’ film screening at UC Berkeley.
More

David Lehrer July 17, 2024
This summer five members of the CBE community received recognition for conference papers and for career contributions, plus travel funding to support conference participation. Three of the awards were presented at the 2024 ASHRAE Annual Conference, and two at Indoor Air 2024. We commend these well-deserved awards and in this post highlight the efforts leading to them.
More

David Lehrer December 19, 2023
As we gear up for our year-end rituals and activities, here at CBE we can take a moment to reflect on our efforts during 2023, and remember our purpose — to contribute towards making a more sustainable and equitable world. We are pleased to report on such wide ranging work, and also note that this would not be possible without the participation of CBE’s Industry Partners. We are grateful for their support and the ongoing contributions of our colleagues, students and affiliates. We wish you all the best for 2024, and in this post share some of our major accomplishments and milestones.
More
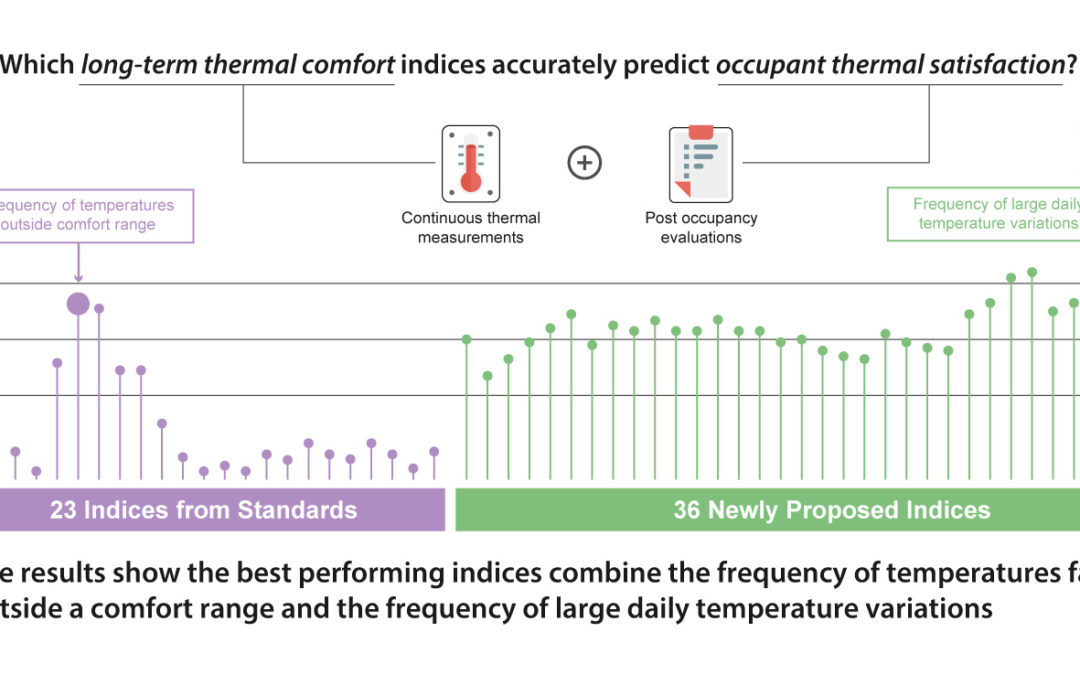
Thomas Parkinson October 12, 2020
An international team of researchers led by CBE has devised a new method for evaluating thermal comfort inside buildings over extended periods of time. The new index, one of many created and tested by the team, has been demonstrated to be a significant improvement over existing indices being used in building design and operation.
More

Edward Arens August 20, 2020
Imagine an ice cream parlor that offers only one flavor of ice cream, one chosen by scientists based on what an ‘average’ person wants. While this idea seems absurd, a similar logic has been used in establishing standards for thermal comfort in buildings. A group of CBE staff, industry partners and others have developed a revision to thermal comfort standards that acknowledges the variability in human comfort preferences.
More

David Lehrer April 15, 2020
Millions of people are working at home to prevent the spread of Covid-19, creating stress and impacting our well-being and productivity. Science shows that time spent in nature may improve our health and emotions, however, when we are not able to be in nature physically, we may derive benefits simply by access to windows with views. A study recently published by CBE found that a view from a window has positive impacts on emotion, cognitive performance and thermal comfort.
More
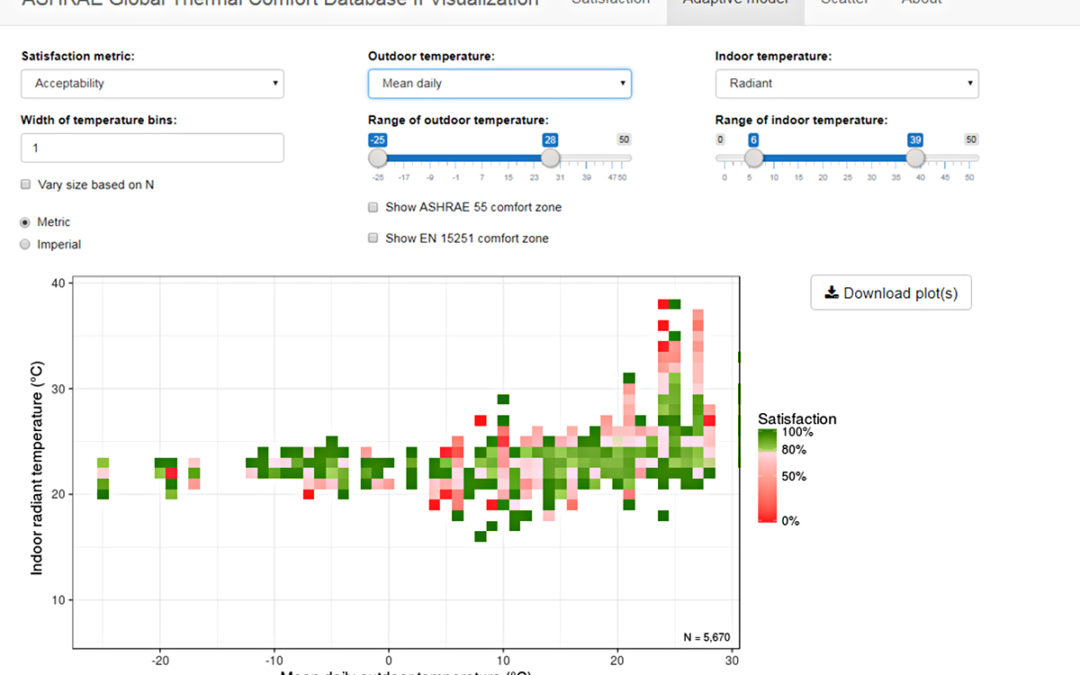
Centerline Team August 20, 2018
We launched a new suite of free and publicly available online resources to facilitate academic and professional studies of thermal comfort in buildings. These tools can be used to inform questions about thermal comfort, and to encourage the design of climate-responsive and comfortable low energy (and ZNE) buildings.
More
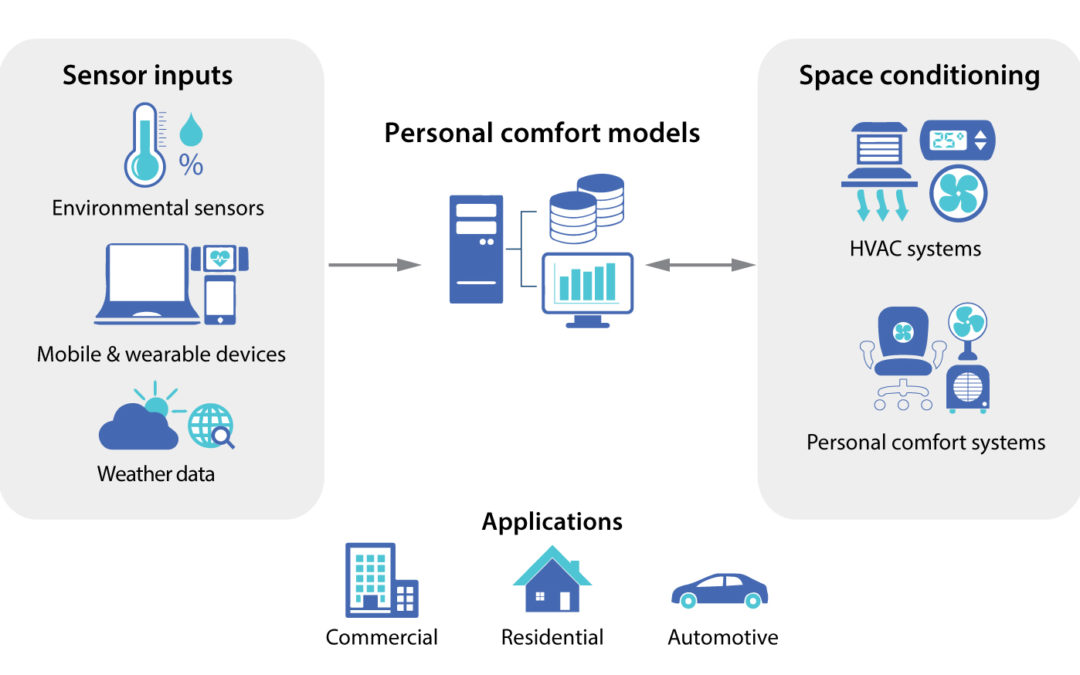
Centerline Team February 15, 2018
The emerging Internet of Things offers opportunities to improve how we design, measure and operate buildings. CBE’s research team conducted a six-month field demonstration of a system using IoT-connected heated and cooled office chairs. Results demonstrated high levels of comfort seen in few buildings. In addition, the data from occupants’ use of the chairs can be used to predict thermal comfort more accurately than methods previously available.
More
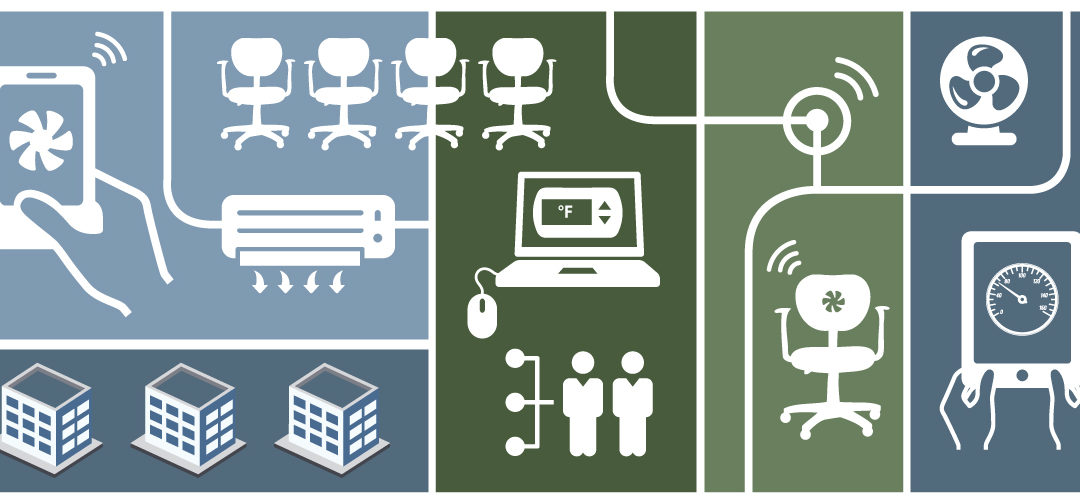
Centerline Team November 28, 2017
CBE’s research team recently completed a project with goals of making buildings occupant-responsive in real time, and addressing outdated rules-of-thumb that lead to poor energy performance and occupant comfort. Findings demonstrated that “personal comfort” chairs led to comfort satisfaction for nearly all test subjects. The project team also developed and tested innovative HVAC control methods offering significant energy saving potential.
More










